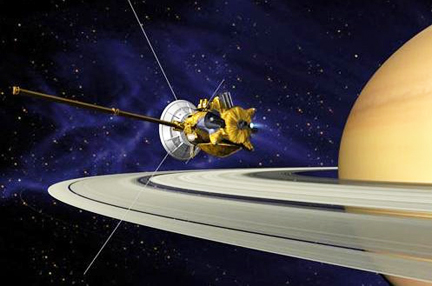
This is a computer-rendered image of Cassini during the Saturn Orbit Insertion (SOI) maneuver, just after the main engine has begun firing. The spacecraft is moving out of the plane of the page and to the right (firing to reduce its spacecraft velocity with respect to Saturn) and has just crossed the ring plane. The SOI maneuver, which is approximately 90 minutes long, will allow Cassini to be captured by Saturn's gravity into a five-month orbit. Cassini's close proximity to the planet after the maneuver offers a unique opportunity to observe Saturn and its rings at extremely high resolution.
The Cassini Solstice Mission will enable continued study of these intriguing worlds. It will also allow scientists to continue observations of Saturn's rings and the magnetic bubble around the planet, known as the magnetosphere. Near the end of the mission, the spacecraft will make repeated dives between Saturn and its rings to obtain in-depth knowledge of the gas giant. During these dives, the spacecraft will study the internal structure of Saturn, its magnetic fluctuations and ring mass.
Cassini entered orbit around Saturn in 2004. Mission managers had originally planned for a four-year tour of the Saturnian system. In 2008, Cassini received a mission extension through September 2010 to probe the planet and its moons through equinox, when the sun was directly over the equator. Equinox, which occurred in August 2009, marked the turn from southern fall to northern spring. The second mission extension, called the Cassini Solstice Mission, was announced earlier this year.

