
Before...Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. (December 7, 2016) - In preparation for launch from Space Complex-37, the Mobile Service Tower or MST is rolled back from the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket carrying the WGS-8 mission for the U.S. Air Force. Photo courtesy of United Launch Alliance
Success can be claimed by United Launch Alliance and the US Air Force as the WGS-8 launch occurred without a hiccup to provide improved communications for the troops, a critical element for their safety.
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket, carrying the eighth installment of the Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) satellite for the United States Air Force, lifted off from Space Launch Complex-37 on December 7th at 6:53 p.m. EDT.
This is ULA’s 11th launch in 2016 and the 114th successful launch since the company was formed in December 2006.
“Thank you to the US Air Force and industry team whose flawless execution enabled today’s successful launch of the WGS-8 mission,” said Laura Maginnis, ULA vice president of Custom Services. "Last week, ULA celebrated our anniversary and 10 years of 100 percent mission success. This evening’s launch epitomizes why our customers continue to entrust ULA to deliver our nation’s most crucial space capabilities.”
This mission was launched aboard a Delta IV Medium+ (5, 4) configuration Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) powered by one common booster core and four solid rocket motors built by Orbital ATK.
The common booster core was powered by an RS-68A liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine producing 705,250 pounds of thrust at sea level. A single RL10B-2 liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine powered the second stage. The booster and upper stage engines are both built by Aerojet Rocketdyne. ULA constructed the Delta IV Medium+ (5,4) launch vehicle in Decatur, Alabama.
WGS-8 marks the sixth flight in the Medium+ (5,4) configuration; all launches in this configuration were WGS missions. WGS-8 supports communications links in the X-and Ka-band spectra. While Block I and II satellites can instantaneously filter and downlink up to 4.410 GHz, WGS-8 can filter and downlink up to 8.088 GHz of bandwidth. Depending on the mix of ground terminals, data rates, and modulation and coding schemes employed, a single WGS satellite can support data transmission rates of more than 6 Gbps.
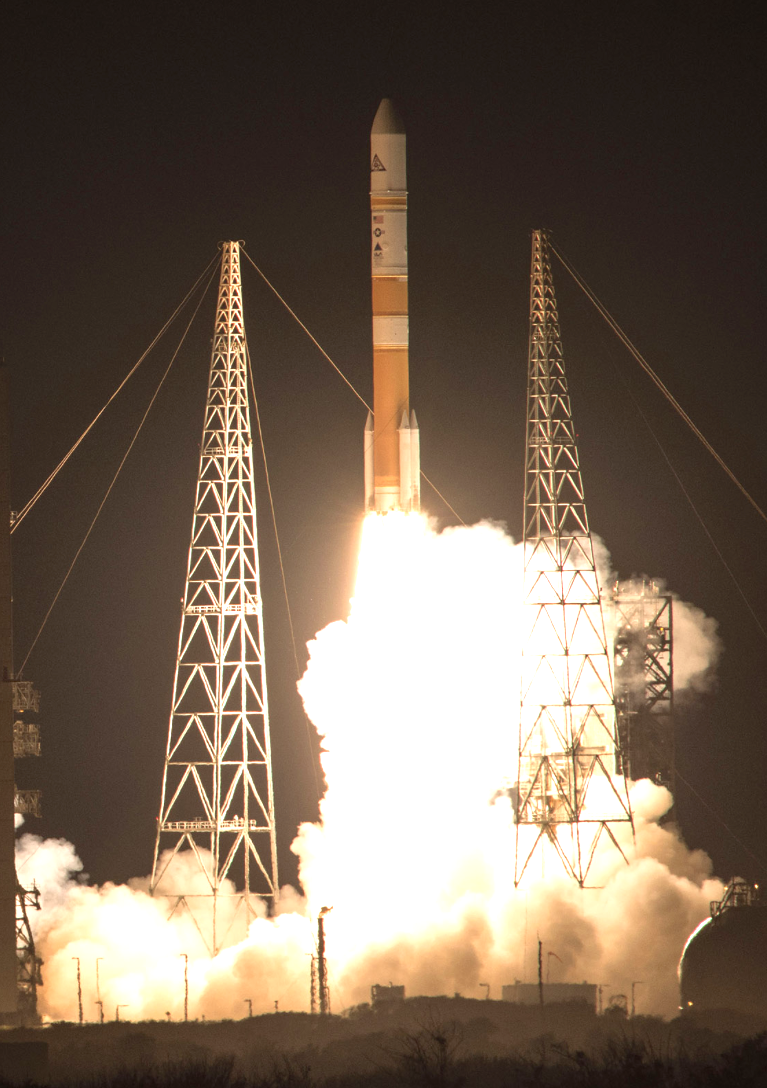

After...Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Floridaa. (December 7, 2016) – A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket carrying WGS-8 mission lifts off from Space Launch Complex-37 at 6:53 p.m. EDT. Photo by United Launch Alliance
WGS-8 with its advanced digital channelizer may support more than 11 Gbps. The current fleet is providing more than 16 Gbps globally and the most heavily loaded WGS vehicle is now locally providing more than 4 Gbps.
WGS has 19 independent coverage areas, 18 of which can be positioned throughout its field-of-view. This includes eight steerable/shapeable X-band beams formed by separate transmit/receive phased arrays; 10 Ka-band beams served by independently steerable diplexed antennas; and one transmit/receive X-band Earth-coverage beam.
WGS can tailor coverage areas and connect X-band and Ka-band users anywhere within its field-of-view. The X-band phased array antenna enables anti-jam functionality without sacrificing performance.
WGS enables more robust and flexible execution of Command and Control, Communications Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (C4ISR), as well as battle management and combat support information functions. The WGS constellation augments the existing service available through the UHF Follow-on satellite by providing enhanced information broadcast capabilities.
Five globally-located Army Wideband SATCOM Operations Centers provide 24/7 payload monitoring and command and control of the WGS constellation. In coordination with the WGS-8 launch, the US Army has modernized the Global SATCOM Configuration and Control Element to a new service-oriented virtualized software system residing on a new ground hardware platform. Each Global Satellite Configuration and Control Element has the capability to control up to 10 WGS satellites at a time.

Spacecraft platform control and anomaly resolution is accomplished by the 3rd Space Operations Squadron at Schriever Air Force Base in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
The EELV program was established by the US Air Force to provide assured access to space for Department of Defense (DoD) and other government payloads.
WGS satellites are an important element of a new high-capacity satellite communications system providing enhanced communications capability to our troops in the field. The commercially developed EELV program supports the full range of government mission requirements, while delivering on schedule and providing significant cost savings over the heritage launch systems.
ULA has successfully delivered more than 110 satellites to orbit that provide critical capabilities for troops in the field, aid meteorologists in tracking severe weather, enable personal device-based GPS navigation and unlock the mysteries of the solar system.
Payload Fairing (PLF)
The PLF is a composite bisector (two-piece shell), 5 meter diameter fairing. The PLF encapsulates the spacecraft to protect it from the launch environment on ascent. The vehicle’s height, with the 47 ft. tall PLF, is approximately 217 ft.
Delta Cryogenic Second Stage (DCSS)
The DCSS propellant tanks are structurally rigid and constructed of formed aluminum plate, spun-formed aluminum domes and aluminum ring forgings. It is a cryogenic liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen-fueled vehicle, powered by a single RL10B-2 engine that produces 24,750 lbf of thrust.
The DCSS cryogenic tanks are insulated with a spray-on insulation and helium-purged insulation blankets. An equipment shelf attached to the aft dome of the DCSS liquid oxygen tank provides the structural mountings for vehicle electronics.
Booster
The Delta IV common booster core (CBC) tanks are structurally rigid and constructed of isogrid aluminum barrels, spun-formed aluminum domes and machined aluminum tank skirts. Delta IV booster propulsion is provided by the throttleable RS-68A engine system which burns cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen and delivers 705,250 lbf of thrust at sea level. The booster’s cryogenic tanks are insulated with a combination of spray-on and bond-on insulation and helium-purged insulation blankets. The booster is controlled by the DCSS avionics system, which provides guidance, flight control.
Solid Rocket Motors (SRM)
Four SRMs generate the additional thrust required for liftoff and attain a combined maximum thrust of 1,124,000 lbs in flight. The SRMs are 5 ft in diameter and 53 ft long and constructed of a graphite-epoxy composite. The SRMs are connected to the booster by two ball-and-socket joints and structural thrusters.

