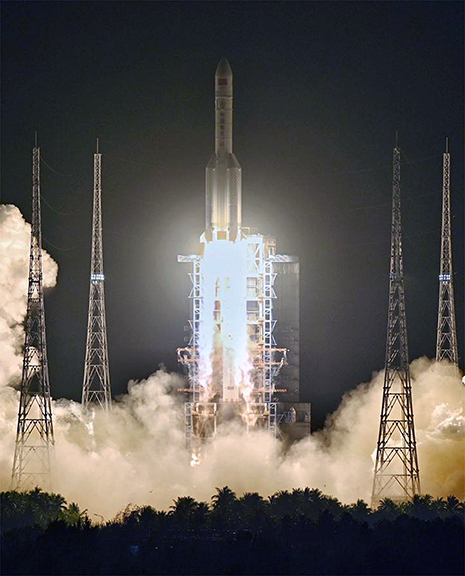

Long March-5 Y3 blasts off from Wenchang Space Launch Center in south China's Hainan Province, December 27, 2019. Launch photo is courtesy of Xinhua/Chen Yehua.
China has launched their third Long March-5, the largest carrier rocket of the country, from Wenchang Space Launch Center in south China's Hainan Province on the evening of December 27, 2019.
The success of the flight lays the foundation for a series of future space projects for the country that include exploring Mars, returning moon samples and constructing the nation's own space station, Wu said. The Shijian-20 satellite will be used to test the key technologies of the DFH-5 platform, China's new-generation large satellite platform, as well as offer communication and broadcasting service, Wu added.
The Long March-5 is a large, two-stage rocket, capable of carrying a payload of 25 tons, equivalent to the weight of 16 cars, to LEO, 14 tons to GEO, eight tons to Earth-Moon transfer orbit, or five tons to Earth-Mars transfer orbit, more than twice the capacity of the current main Long March series rockets. Combined with an upper stage, the rocket is capable of sending probes to explore Jupiter and other planets in the solar system, according to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
Compared with the Long March-5 Y2, the new rocket has more than 200 technological improvements, said Yang Hujun, deputy chief designer of the rocket. The modified engine has undergone more than 10 ground tests lasting over 3,000 seconds in total.
Wang Jue, Chief Commander of the research team, noted that over the past two years, the research team has solved the problem of the engine and improved the reliability of the rocket.
The rocket is about 57 meters long, equivalent to the height of a 20 story building, with a 5 meter diameter core stage and four, 3.35 meter diameter boosters. The Long March-5 has a takeoff weight of about 870 tons and a thrust of more than 1,000 tons.
The carrying capacity of the Long March-5 rocket equals that of other mainstream large-scale rockets in the global industry, greatly improving China's ability to launch spacecraft and laying the foundation for developing new-generation carrier rockets and heavy-lift launch vehicles, said Wang Xiaojun, head of the CALT.

China's Shijian-20 satellite. Photo is courtesy of CASC.
Of additional interest is the Xinhua posting that reports China will finish the construction of the BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3), with another two geostationary orbit satellites to be launched, before June 2020, said BDS Spokesperson Ran Chengqi on Friday.
Ran said at a press conference of the State Council Information Office that with the BDS as the core, a more ubiquitous, integrated and intelligent navigation and timing system with comprehensive national positioning is scheduled to be established by 2035.
China sent 10 BDS satellites into space during 2019. The deployment of the core BDS-3 constellation system has been completed with all of the BDS-3 system's medium earth orbit satellites being networked. With the system's upgraded intelligent operation and maintenance capabilities, the BDS-3 has provided stable and accurate services, boasting a positioning accuracy of better than five meters.
The BDS system has multiple service capabilities, including satellite-based augmentation, short message communication, ground augmentation as well as international search and rescue. It will provide more diversified services with better performance and higher accuracy in 2020, Ran said.
A series of documents on the BDS system were also released to promote the understanding of the system and facilitate its use. The documents were published on the official website of the Beidou Navigation Satellite System. The BDS system has seen thriving applications in many areas and has fostered an industrial ecosystem, Ran said.
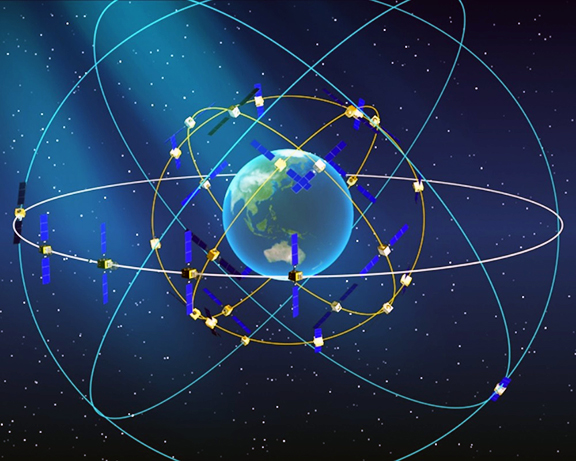
Artistic rendition of China's Beidou satellite navigation constellation. This image is courtesy of beidou.gov.cn
The 22nm process navigation and positioning chip supporting BDS-3's new signal has a smaller volume, lower power consumption and higher accuracy, and has realized large-scale application. The new generation of BDS system-related products including high-precision antennas, boards, and broadband radio frequency chips has been developed.
The BDS system has also seen increasing applications in emerging fields such as the industrial Internet and Internet of Things, as well as autonomous driving, parking and logistics. With the arrival of the 5G commercial era, BDS is accelerating the integration with new technologies such as the next generation of mobile communication, blockchain and artificial intelligence, Ran said.
The BDS system is playing an important role in many industries including transportation, agriculture, forestry and energy. It supports China's dynamic monitoring system for more than 6.5 million vehicles. It will further facilitate railway transportation, inland river shipping, ocean navigation and the management of transportation infrastructure construction, Ran said, adding thaty China is continuously promoting the development of a legal system for satellite navigation.
China's applications for satellite navigation patents have increased rapidly and the number has reached 70,000, ranking first in the world.
More BDS-related national standards and special standards will be released to ensure a sound environment for its industrial application, Ran added.
Article source: Xinhua

