
After the CanX-7 smallsat deployed its drag sails only a week ago, early results indicate the sails are having a noticeable effect.
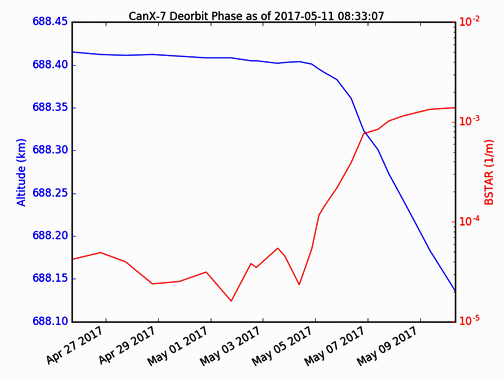
Space Flight Laboratory (SFL), which developed CanX-7, has announced the altitude decay rate changed significantly following the deployment in the late evening of May 4, 2017 (Toronto time). The following graph of the altitude decay rate illustrates the aerodynamic drag on the satellite has increased as a result of a changed ballistic coefficient. SFL expects that after a certain amount of time CanX-7 will aerodynamically stabilize due to the so-called “shuttlecock” effect, with all four sails to the rear of the satellite as it travels around Earth.
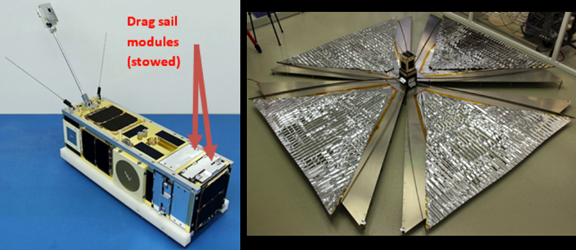
The CanX-7 deorbiting demonstration is intended to space qualify SFL-developed drag sail technology. The technology can then be used with confidence to ensure that small satellites comply with Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) guidelines for space debris mitigation. This is an important technology for ensuring that the environment is kept safe for future generations of LEO missions.
“This is an earlier-than-expected positive result from CanX-7,” explained Dr. Robert Zee, the SFL Director. “It confirms and validates the effectiveness of the drag sails in accelerating orbital decay.”

