
Thales Alenia Space, the joint venture between Thales (67 percent) and Leonardo (33 percent), is presenting cameras developed by its Swiss subsidiary for the ExoMars 2020 program: two wide angle cameras (WAC) and the close-up imager (CLUPI).
The two wide angle cameras (WAC), developed by Thales Alenia Space in Switzerland as prime contractor, will be directly integrated in PanCam (The Panoramic Camera provided by European labs and universities), one of the instruments mounted on the ExoMars 2020 rover. PanCam will deliver images in the visible and near infrared wavelengths.

Thales Alenia Space's PanCam.
The PanCam instrument, fitted with 12 filters, will be installed on the rover's mast. It will provide multi-spectral stereo images over a field of view of 38.3° (horizontal/vertical). The camera faces a daunting design challenge because of the wide range of temperatures it will experience, from -130° C (in survival mode) in the Martian environment, to +110° C because of the need for biological sterilization to protect the planet.
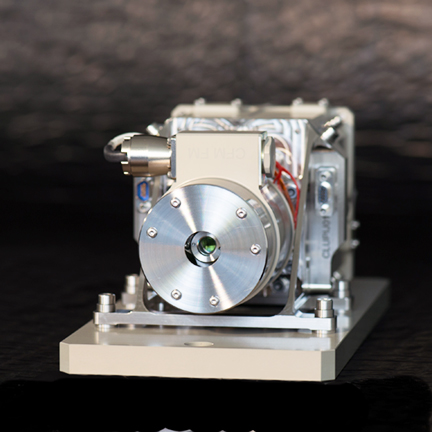
Thales Alenia Space's CLUPI close up imager for the
ExoMars 2020 mission.
The close-up imager (CLUPI) will be mounted directly on the drill arm, to provide close-up images of the Martian terrain, including surrounding rocks, soil and cliffs. It can focus at distances from 11.5 centimeters to infinity. This camera also features a focus stacking function, which entails combining several images with different focal planes depending on the distance, to transmit an image offering greater depth of field. The CMOS (Complementary metal-oxide- semiconductor) photographic detector offers resolution of 2652 pixels x 1768 pixels.
This productive collaboration between industry and academia was made possible thanks to ESA's scientific experiment development program, PRODEX (Programme de Développement d'Expériences scientifiques).
Based in Zurich, Thales Alenia Space in Switzerland is specialized in the engineering and production of complex and innovative instruments for scientific and Earth Observation (EO) satellites, as well as spaceborne optical communications terminals.
Through the design and construction of these two types of cameras, Thales Alenia Space once again proves its ability to develop highly specialized and sophisticated instruments. Thales Alenia Space in Switzerland has contributed to a number of European space missions, for example by developing the telescope for the CaSSIS instrument on ExoMars, the receiver for the laser altimeter on BepiColombo, and electronics for the inertial sensor on LISA Path Finder.
ExoMars is an European Space Agency program executed in cooperation with Russian Space Agency Roscosmos with contribution of NASA. The chronology can be summarized as follows: Launch from Baikonur between 26 July and 11 Aug 2020, cruise to Mars through a direct ballistic trajectory, separate the CM from DM, entry into the Martian atmosphere and the subsequent descent and landing of the Descent Module and its Rover, weighing approximately 2 metric tons, on 19 March 2021; the arrival of a landing platform and egress of the rover; exploration by the rover of a vast area of Mars, with geological/scientific sampling of both the planet's surface and subsoil, by taking and analyzing soil samples to a depth of 2 meters; search for present or past forms of life in the soil samples that will be processed on the spacecraft; geochemical and atmospheric studies of the surface and underground environments.
On the 2020 mission, Thales Alenia Space in Italy, is in charge of the design, development and verification of the entire system, the development of the Carrier Module navigation and guidance system and perform EDL/GNC development, the Rover System, including the Analytical Laboratory Drawer (ALD) as well as supplying basic parts of the DM, including the Radar Altimeter. In addition, Thales Alenia Space in Italy implements a deep technical partnership with Lavochkin (RUS) with European contributions for the development Descent Module (DM) Kazachok. OHB is in charge to develop the Carrier Module (CM) as well as some ALD subsystems (SPDS Mechanisms, Structure and Harness).
The Rover Vehicle itself is provided by Airbus Defence and Space in UK. Leonardo is developing the ExoMars drill, which will dig into the Mars subsoil at a depth of two meters plus the Drill and ALD mechanisms control unit and software. ALTEC — Aerospace Logistics Technology Engineering, a Thales Alenia Space in Italy (63.75 percent), and ASI (36.25 percent) company — will also be responsible for the design, development and maintenance of the ROCC (Rover Operation Control Center) and for controlling the Rover on the Martian surface.

