
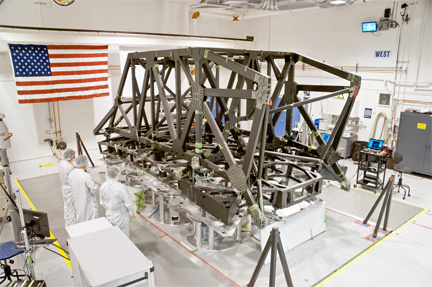
Technicians complete the center section of the backplane and backplane support frame for NASA's James Webb Space Telescope at ATK's facility in Magna, Utah. Photo Credit: ATK
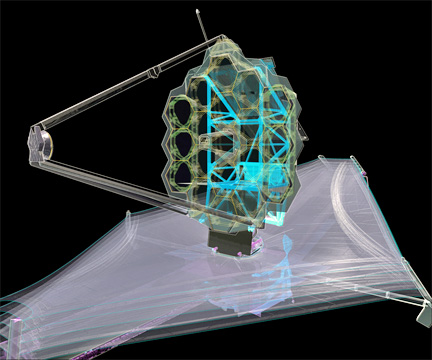
This x-ray diagram of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope shows where the backplane support frame (BSF) is in relation to the whole observatory. The BSF is the backbone of the observatory, is the primary load carrying structure for launch, and holds the science instruments.
Photo Credit: Northrop Grumman
"This is the largest optically stable cryostructure that has ever been built," said Gregory Young, Acquisition manager for Northrop Grumman. "With the completion of the frame, the structural backbone of the observatory is now ready for integration."
Measuring approximately 24 ft. tall by 19.5 ft. wide by more than 11 ft. deep when fully deployed, and weighing only 2,180 lbs., the fully assembled primary mirror backplane support structure will include the wing assemblies, the center section and the BSF. This fully populated PMBSS will support the mission payload and instruments weighing more than 7,300 lbs., or more than 300 percent its own weight.
The highly efficient PMBSS will also meet unprecedented thermal stability requirements to minimize thermal distortion. While the telescope is operating at a range of extremely cold temperatures, from -406 to -343 degrees Fahrenheit, the backplane must not vary more than 38 nanometers (approximately 1/1,000 the diameter of a human hair). For reference, if the mirror were enlarged to span from Los Angeles to New York City, the tolerance for error would be less than 1 inch.
The BSF was designed and fabricated at ATK facilities in Magna, Utah. ATK designed, engineered and constructed the more than 10,000 parts of the entire PMBSS using lightweight graphite materials, state-of-the-art material sciences and advanced fabrication techniques. The composite parts attach in many cases to precision metallic fittings, made of materials such as invar and titanium that provide interfaces with other elements of the observatory.
"It is truly inspiring to participate in ideas that lead to invention and finally this fantastic reality of the PMBSS assembly," said Bob Hellekson, ATK's Webb Telescope program manager. "It continues to be a privilege and an honor for the ATK team to provide program hardware that is arguably the largest and most advanced cryogenic structure ever built."
ATK has begun final integration of the BSF to the previously completed center section. The newly assembled structure is on track to meet critical path program milestones when it is delivered to Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. later this summer for the extreme cryogenic thermal testing. The PMBSS will then undergo structural static testing at Northrop Grumman's facilities in Redondo Beach, Calif. in early 2014 before NASA and Northrop Grumman ready the observatory for its 2018 launch.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's next-generation space observatory and successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. The most powerful space telescope ever built, the Webb Telescope will observe the most distant objects in the universe, provide images of the first galaxies formed and see unexplored planets around distant stars. The Webb Telescope is a joint project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.

