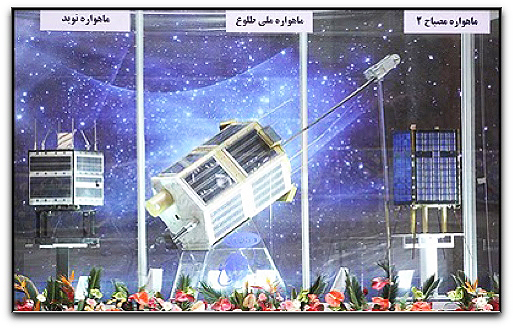
New Iranian satellites — photo Iranian News Service
The new satellites set for launch include the Toloo (Dawn) imaging satellite, a 220 lb. rectangular-shaped satellite that is the largest of Iran's new spacecraft, which may be launched as early as this month or in March, the Iranians said. The satellite will be launched into a 300 mi. orbit and is designed to operate for three years and was built by the Iran Electronics Industries Co. It may well be a dual-use payload for civil and military ground imaging purposes. But even a medium resolution system would enable Iran to better target military sites in Israel, such as the Israeli Arrow anti-ballistic missile facilities.
The second is the Navid (Good News) communications satellite — this low altitude spacecraft has been developed, in part, by engineering students and is designed to provide store and forward communications services.
The third satellite is Mesbah-2, another store and forward communications satellite design that's planned for launch during 2011.
The new Simorgh ICBM is being developed into a two-stage launch vehicle. This booster and its upper stage have more relevance to ICBM range extension than does the Safir, which launched the Omid satellite in 2009. The Simorgh rocket is 89 ft. long, and has a mass of 85 tons. Its first stage uses a four nozzle propulsion system with 290,000 lb. of liftoff thrust. The Iranians did not provide any significant information on the vehicle's upper stage, possibly because that directly involves use of the same configuration for an ICBM. (Source: Spaceflight Now)

